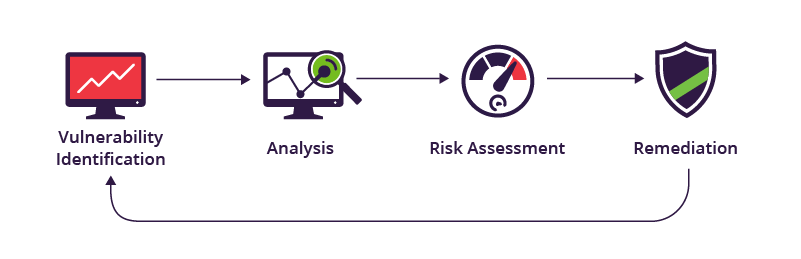
Vulnerability management automation refers to the use of automated tools and processes to identify, assess, prioritize, and remediate security vulnerabilities in IT systems. This approach aims to streamline and enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of vulnerability management programs, reducing the risk of cyber attacks and improving overall security posture.
In this blog, we will be looking at the challenges of traditional vulnerability management which makes it a necessity to make the use of Automation in Vulnerability management. We will also be looking at the key components of Automated Vulnerability Management and it’s benefits.
Challenges of traditional vulnerability management
- Using Manual tools to find vulnerabilities:
Traditional vulnerability management methods make the use of manual process to find vulnerabilities. This manual process is really slow compared to automated ones. Manual methods are time consuming and this can lead to outdated observations about your attack surface, instead of real-time insights. For example: If a vulnerability scan is performed manually on a monthly basis, any new vulnerabilities that emerge in the weeks following the scan will remain undetected until the next scan. This gap leaves the system exposed.
- Using Multiple Security Tools:
In traditional vulnerability management methods, a company might spend excessively on multiple security tools. This often creates chaos and waste of time, inhibiting the security team’s efficiency.
- Incomplete asset inventory:
Today, the organizations have thousands of assets, including devices, databases, third-party components and cloud assets, creating a large attack surface for attackers. Managing all these assets in spreadsheets fail to provide an accurate picture of enterprise assets. Also, after a security review, critical assets might be unidentified or improperly tagged, increasing cyber risk.
- Lack of real-time coverage:
Traditional tools cannot analyze the enterprise attack surface in real-time. Periodic scans (often monthly) result in vulnerability data that is several days or weeks old. This puts the organizations at a high risk.
- Delayed Response and Dynamic Threats:
Once vulnerabilities are discovered, they are patched manually in traditional vulnerability management methods. This results in slower dispatch and response times. Also, New vulnerabilities and changing network environments require continuous analysis, which traditional methods cannot provide.
Why automate vulnerability management?
Now that we have looked at the flaws in traditional vulnerability management methods, we can say that increasing size and complexity of infrastructure and networks, coupled with the rapid rise in cyber attacks it is important to use Automated Vulnerability Management Solutions. Manual methods can no longer keep up with the need to accurately identify assets, discover new vulnerabilities, and prioritize and remediate threats promptly. Automated solutions not only increase efficiency but also provide real time analysis of all the assets in an organization.
Key components of Automated Vulnerability Management Solutions:
1) Identification

Identification of vulnerabilities has two major parts:
Data Collection: This involves Gathering information about the organization’s assets, including hardware, software, networks, and applications. This involves inventorying all components that need to be assessed.
Vulnerability Scanning: Using automated tools to perform scans and identify known vulnerabilities based on signatures, configurations, and behavior analysis.
Vulnerability scanning is an automated process that systematically examines an organization’s IT infrastructure to identify security vulnerabilities. These vulnerabilities may include software bugs, misconfigurations, and other weaknesses that could be exploited by attackers.
Key Aspects of Vulnerability Scanning:
- Automated, Continuous Scanning:
Regular Intervals: Scans are conducted at regular intervals (daily, weekly, or monthly) to ensure continuous coverage and up-to-date information.
Real-Time Scanning: Some systems provide real-time or near-real-time scanning capabilities to detect vulnerabilities as soon as they arise.
2. Credentialed vs. Non-Credentialed Scanning:
Credentialed Scanning: Involves using authorized access credentials to perform a more thorough and comprehensive scan. This method can access deeper layers of the system, identify configuration issues, and detect vulnerabilities that require authenticated access.
Non-Credentialed Scanning: Performs scans without using any access credentials. This method simulates the perspective of an external attacker and can identify vulnerabilities visible without authentication, such as open ports and services.
Types of Vulnerability Scans:
- Network Scans: Focus on network devices such as routers, switches, and firewalls to identify vulnerabilities like open ports, insecure protocols, and misconfigurations.
- Application Scans: Target web applications and software to detect issues such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and other application-specific vulnerabilities.
- Host Scans: Examine servers, workstations, and other endpoints for operating system vulnerabilities, outdated software, and insecure configurations.
- Database Scans: Assess database systems for vulnerabilities related to data storage, access controls, and SQL injection.
Scanning Methodologies:
- Signature-Based Detection: Uses a database of known vulnerabilities and their signatures to identify issues. This method is effective for detecting well-known vulnerabilities but may miss new or unknown threats.
- Behavioral Analysis: Analyzes the behavior of systems and applications to identify anomalies that may indicate vulnerabilities. This method can detect unknown or zero-day vulnerabilities.
- Configuration Analysis: Examines system and application configurations to ensure they adhere to security best practices and standards.
2) Analysis and Prioritization in Vulnerability Management

Analysis in vulnerability management involves evaluating identified vulnerabilities to understand their potential impact on an organization’s IT environment. This process assesses the severity, risk, and context of each vulnerability, providing the basis for informed decision-making and effective remediation strategies. This analysis is directly linked with the Prioritization step. Prioritization in vulnerability management involves ranking identified vulnerabilities based on various factors such as severity, criticality of affected assets, exploitability, and potential impact. The goal is to address the most critical vulnerabilities first to effectively reduce risk and enhance the organization’s security posture.
Key Components of Vulnerability Analysis and prioritization:
- Contextual Analysis
Environmental Context: Understanding the specific IT environment in which the vulnerability exists, including the type of system, application, and network configurations. This helps in assessing how a vulnerability might be exploited in that particular setting.
Business Context: Evaluating the potential impact of a vulnerability on the organization’s business operations. This includes considering the role of the affected asset, its importance to business continuity, and potential financial and reputational damage.
2. Assessment:
Severity Assessment: Using standardized scoring systems like the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) to rate the severity of vulnerabilities. CVSS scores take into account factors like exploitability, impact, and complexity.
Likelihood of Exploitation: Assessing how likely it is that a vulnerability will be exploited. This involves considering factors such as the availability of exploit code, the ease of exploitation, and the presence of active threats targeting the vulnerability.
Impact Analysis: Determining the potential consequences of a vulnerability being exploited. This includes evaluating the possible effects on data integrity, confidentiality, availability, and overall business operations.
3. Asset Criticality
Asset Inventory: Maintaining a detailed inventory of all assets, including their configurations and roles within the organization. This helps in assessing the criticality of each asset and the potential impact of vulnerabilities affecting them.
Criticality Assessment: Evaluating the importance of each asset to the organization’s operations. Critical assets, such as those supporting key business processes or containing sensitive data, are prioritized for remediation.
4. Exploitability:
Exploit Availability: Checking if there are known exploits or exploit kits available for the vulnerability. Publicly available exploits increase the risk associated with the vulnerability.
Ease of Exploitation: Assessing how easy it is to exploit the vulnerability. This includes considering the required skill level, necessary tools, and conditions for successful exploitation.
Benefits of Effective Prioritization:
- Efficient Resource Allocation: By focusing on the most critical vulnerabilities first, organizations can allocate their resources more effectively and efficiently.
- Reduced Risk: Addressing the highest-risk vulnerabilities promptly reduces the overall risk to the organization and enhances its security posture.
- Improved Decision-Making: Clear prioritization provides actionable insights that support informed decision-making and strategic planning.
- Compliance: Effective prioritization helps organizations meet regulatory and compliance requirements by demonstrating a systematic approach to vulnerability management.
- Enhanced Resilience: Proactively addressing critical vulnerabilities improves the organization’s resilience to cyberattacks and other security threats.
3) Remediation

Remediation in vulnerability management involves taking actions to fix or mitigate identified vulnerabilities in an organization’s IT infrastructure. This process ensures that vulnerabilities are addressed in a timely and effective manner to reduce the risk of exploitation and enhance the overall security posture of the organization.
Key Components of Remediation:
- Automated Patch Management
Implementing systems that automatically apply patches to vulnerable software and systems. Automated patch management tools can schedule and deploy patches across the network, ensuring that updates are applied consistently and promptly.
2. Configuration Changes
Hardening Configurations: Applying security best practices to system and application configurations. This includes disabling unnecessary services, changing default settings, and enforcing strong authentication and authorization mechanisms.
Continuous Configuration Monitoring: Regularly monitoring and auditing configurations to ensure they remain secure and compliant over time.
3. Validation and Verification
Post-Remediation Testing: This involves verifying that remediation actions have been effectively implemented and that vulnerabilities have been resolved. This may involve re-scanning, manual testing, or both.
Benefits of automated vulnerability management:
- Efficiency: Automation streamlines cybersecurity operations by automating repetitive tasks such as vulnerability scanning, patch deployment, and compliance reporting. By automating these routine processes, security teams are freed from manual, time-consuming activities. This allows them to redirect their focus towards more strategic initiatives, such as threat analysis, incident response planning, and improving overall security posture. As a result, organizations can optimize their resources and improve operational efficiency across their cybersecurity efforts.
- Speed: Automated vulnerability management tools enable organizations to quickly identify and address vulnerabilities across their IT infrastructure. These tools can perform continuous scanning and monitoring, detecting vulnerabilities as soon as they arise. Automated processes facilitate rapid response times for vulnerability remediation by automating the deployment of patches and security updates.
- Accuracy: Automation significantly enhances accuracy in vulnerability management practices. By reducing human intervention in routine tasks, automation minimizes the risk of errors such as misconfigurations or oversight during vulnerability assessments and remediation efforts.
- Scalability: Automated vulnerability management tools are designed to handle large and complex IT environments effectively. These tools can scale to accommodate the growing volume of data, devices, and networks within an organization. Whether managing numerous endpoints, diverse cloud environments, or hybrid infrastructures, automation provides the scalability needed to perform comprehensive vulnerability scanning and management across the entire IT landscape. This scalability ensures that organizations can maintain robust security measures without compromising performance or responsiveness.
- Continuous Monitoring: Automation enables continuous monitoring of vulnerabilities, providing real-time visibility into the organization’s security posture. Automated systems can continuously scan and assess the network for new vulnerabilities and potential security threats. This proactive approach allows security teams to stay ahead of emerging risks by receiving immediate alerts and notifications when vulnerabilities are detected. Continuous monitoring ensures that organizations have up-to-date information on their security status, enabling timely response and mitigation actions to minimize the impact of potential cyber threats.
Conclusion
Automation in vulnerability management offers significant advantages across efficiency, speed, accuracy, scalability, and continuous monitoring. By leveraging automated tools and processes, organizations can enhance their cybersecurity resilience, mitigate risks effectively, and maintain proactive security measures in today’s dynamic threat landscape.
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/aspiainfotech/
Website: https://aspiainfotech.com/