Understanding the danger posed by vulnerabilities is essential for cybersecurity and here CVSS comes into play. CVSS or Common Vulnerability Scoring System is a framework used to evaluate the severity of security vulnerabilities. It uses a set of metrics to calculate a score that represents the severity of that vulnerability. This methodology is employed to gauge how serious vulnerabilities are in the software systems.
The severity score of a vulnerability can be calculated using the CVSS calculator.It considers some variables, including the complexity of the attack, the level of access needed to exploit the weakness, and the potential effects on the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the system.
Benefits of CVSS
For the cybersecurity community, the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) has a number of advantages, including:
- Consistency:
For evaluating the seriousness of vulnerabilities across many organizations and systems, it offers a defined, consistent method. - Prioritization:
It enables security experts to rank vulnerabilities in order of severity, enabling them to concentrate their resources and efforts on the most serious flaws. - Communication:
By using it, security teams can clearly and consistently convey to other teams and stakeholders the seriousness of vulnerabilities, ensuring that everyone is aware of the risks and capable of taking the necessary action. - Automation:
By simply integrating it into vulnerability management tools and procedures, vulnerability management can be done more quickly and automatically.
CVSS vs. CVE
CVSS(Common Vulnerability Scoring System) and CVE(Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures) are related concepts in cybersecurity.
The CVE system offers a standard approach for locating and naming security flaws in hardware and software systems. Contrarily, CVSS is a framework that offers a standard method of evaluating the seriousness of vulnerabilities.
While CVE offers a unique identifier for a vulnerability, CVSS offers a mechanism to assess that vulnerability’s severity. Together, the two approaches provide a standardized method of determining and communicating the severity of vulnerabilities, with CVSS scores frequently being linked to CVE Identifiers.
Hence, CVE provides a way to identify and track vulnerabilities, while CVSS provides a way to assess the severity of those vulnerabilities.
CVSS Calculator versions
There are currently three versions of CVSS:
- CVSS v1 calculator: This was released in 2005 and is no longer supported.
- CVSS v2 calculator: The 2007 version of CVSS, version 2, is still frequently used. It has a base score span from 0 to 10 and considers three factors: availability, confidentiality, and integrity.
- CVSS v3 calculator: The most recent version of CVSS, CVSSv3, was released in 2015. It incorporates various new measures, such as attack vectors, attack complexity, and privileges required, and has a base score that runs from 0 to 10.
**It is advised to use CVSSv3 when evaluating vulnerabilities because it is thought to be more thorough and accurate than earlier versions.
CVSS Metrics
CVSS uses a set of metrics to evaluate the severity of a vulnerability. These metrics are used to calculate the Base Score, which is a numerical value that represents the severity of a vulnerability on a scale from 0 to 10. Three metrics are used:
Base metrics
The vulnerability’s core attributes, such as the difficulty of gaining access, the need for authentication, and the effect on confidentiality, integrity, and availability, are assessed using the base metrics.
These metrics are used to calculate the vulnerability’s baseline score.
The Base Score breakdown includes
- 0.0 = No threat to the system
- 0.1-3.9 = Low
- 4.0-6.8 = Medium
- 7.0-8.9 = High
- 9.0 – 10.0 = Critical
The CVSS Base Score includes two subscores, Exploitability and Impact.
The Exploitability Subscore is derived from the individual vulnerable component. It includes
- Attack Vector —which ranks how difficult for hackers to target the vulnerability.
- Attack Complexity —which ranks the environment, a hacker must overcome to attack the vulnerability.
- Privileges Required — which ranks the level of credentials, a hacker must use to exploit the vulnerability.
- User Interaction — which ranks how difficult a target is to hack without the aid of additional users.
The Impact Subscore is used to determine the severity of vulnerable individual components in a successful attack. It includes
- Authorization Scope — which ranks the degree of impact a component can have.
- Confidentiality — which ranks the level of authority that an exploit gives to an attacker.
- Integrity — which ranks the degree of modifiable data offered by an exploit.
- Availability — which ranks the loss of availability to an exploitable resource.
Temporal metric
The temporal metrics are used to assess how a vulnerability has changed over time, such as whether a patch is available or whether an exploit exists.
These metrics are employed to modify the vulnerability’s baseline score.
It includes three metrics:
- The Exploit Code Maturity — which ranks the likelihood an exploit will be leveraged based on existing scripts found online.
- Remediation Level — which ranks the ease with which an exploit can be remediated.
- Report Confidence — which ranks the reliability that vulnerability exists.
Environmental metrics
The environmental metrics are used to assess the vulnerability’s effects on the particular environment where it exists, such as the potential cost to assets or the worth of the data that has to be secured.
These metrics are employed to further modify the vulnerability score. Environmental metrics are modifiers of the base group.
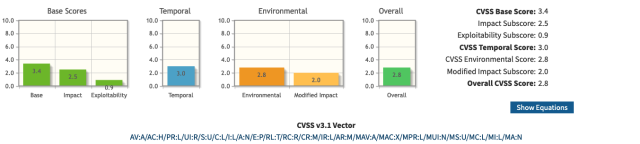
The CVSS calculator generates a score ranging from 0 to 10, with 10 being the most severe, once all the metrics have been evaluated. It’s important to note that the CVSS calculator offers a helpful framework for assessing vulnerabilities. The results of the calculator may not fully reflect the risk connected to a vulnerability in a given context because they are dependent on a number of assumptions.
Calculating CVSS
There are a lot of free CVSS calculators available online. Let’s calculate the CVSS score from this calculator https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln-metrics/cvss/v3-calculator.
Just select all the vectors of the base score, temporal and environmental metrics and it will automatically calculate the score for you.
It’s important to note that the scores are computed in a sequence that the Base Score is used to calculate the temporal Score and the temporal Score is used to calculate the environmental Score.
Best practices for using CVSS
- Use CVSS in combination with other security assessment techniques such as penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and threat modeling. It can help organizations to improve their vulnerability management processes, reduce their risk exposure, and enhance their overall cybersecurity posture.
- When using CVSS scores to make decisions about remediation priorities, it is important to consider the specific context. This includes factors such as the system’s criticality, the potential impact of an exploit, and the ease of exploitation.
CVSS and compliance
- Some regulatory frameworks require the use of CVSS scores: Certain regulatory frameworks, such as PCI DSS, require organizations to use CVSS scores to prioritize vulnerability remediation efforts. It has become the standard way to rank the severity and protection of the system based on these scores.
- Ensure alignment with relevant regulations and standards: When using prioritization using CVSS, it is important to ensure that it aligns with the requirements of relevant regulations and standards. This includes ensuring that the CVSS scores are being used correctly and that the remediation efforts are appropriate.
Limitations of CVSS
- Does not account for real-world exploitation: As told earlier, the results of the calculator may not fully reflect the risk connected to a vulnerability being exploited in the real world. This means that vulnerabilities with high CVSS scores may not necessarily be the most critical from a real-world perspective.
- May not account for specific context: CVSS scores are dependent on several assumptions. For example, a vulnerability that affects a custom system may be more severe than one that affects a less important system, even if they both have the same CVSS score which could impact the severity of a vulnerability in a particular context.
Conclusion
The CVSS calculator is a valuable tool in the field of cybersecurity that helps organizations prioritize their efforts to remediate vulnerabilities. However, it should be used in conjunction with other risk management practices to ensure that vulnerabilities are addressed effectively.





